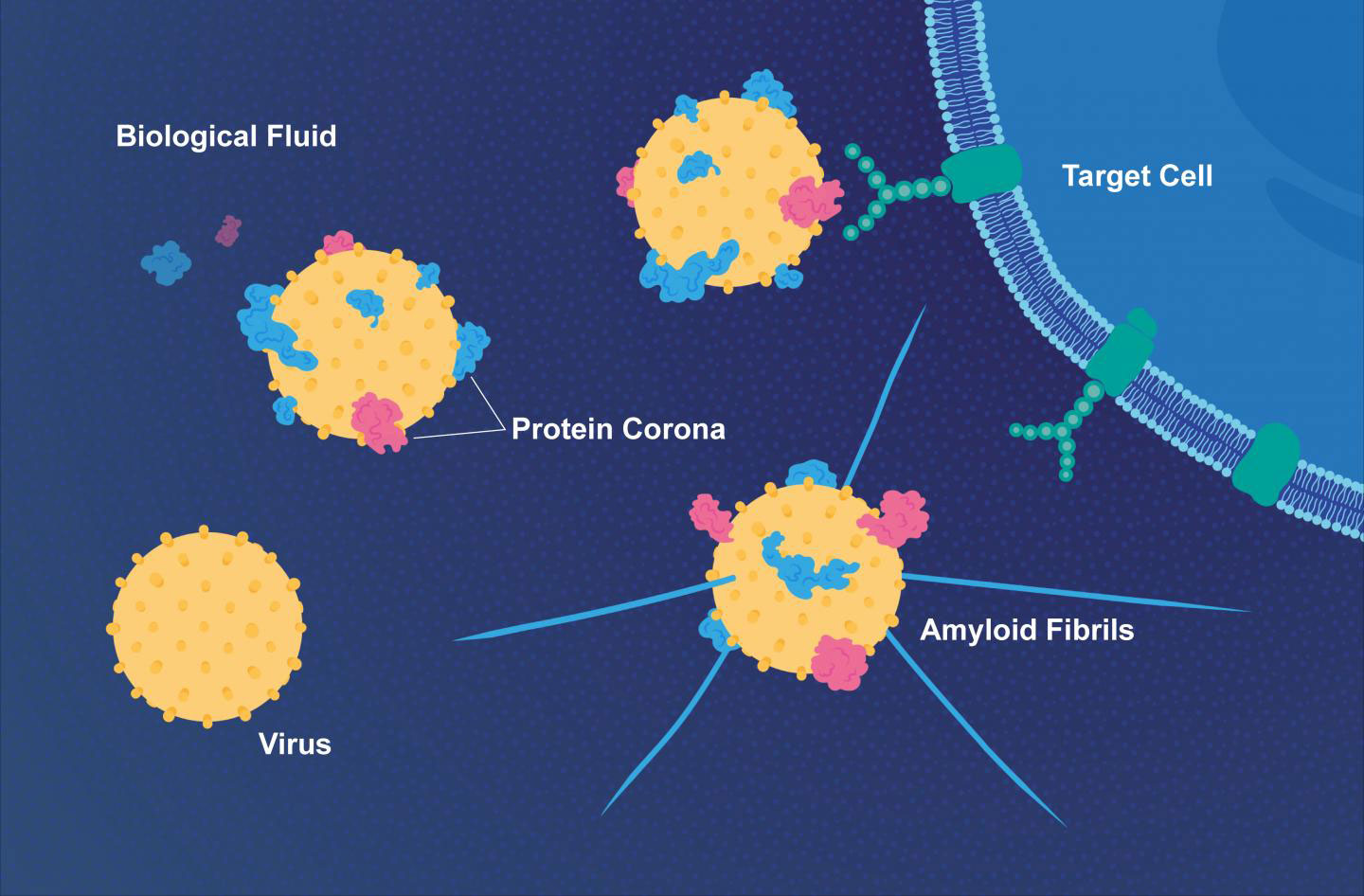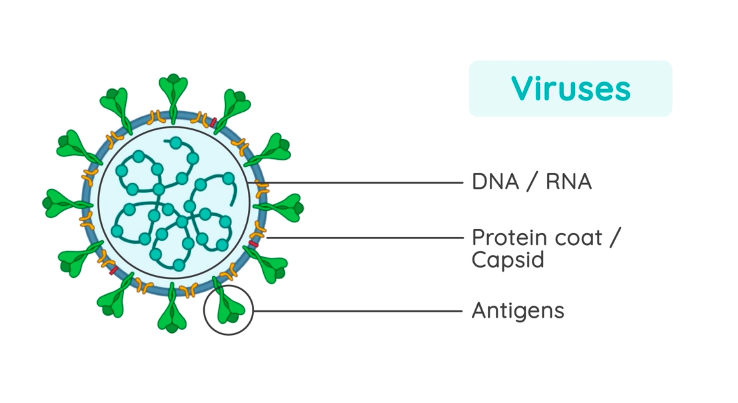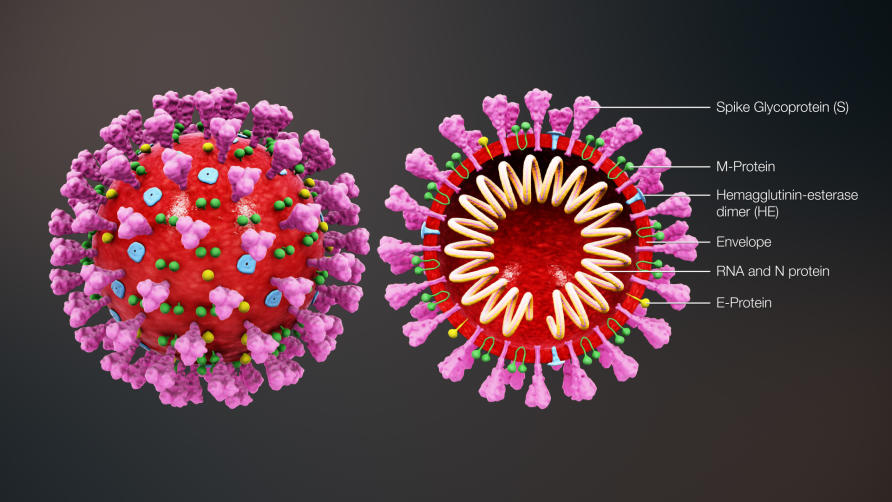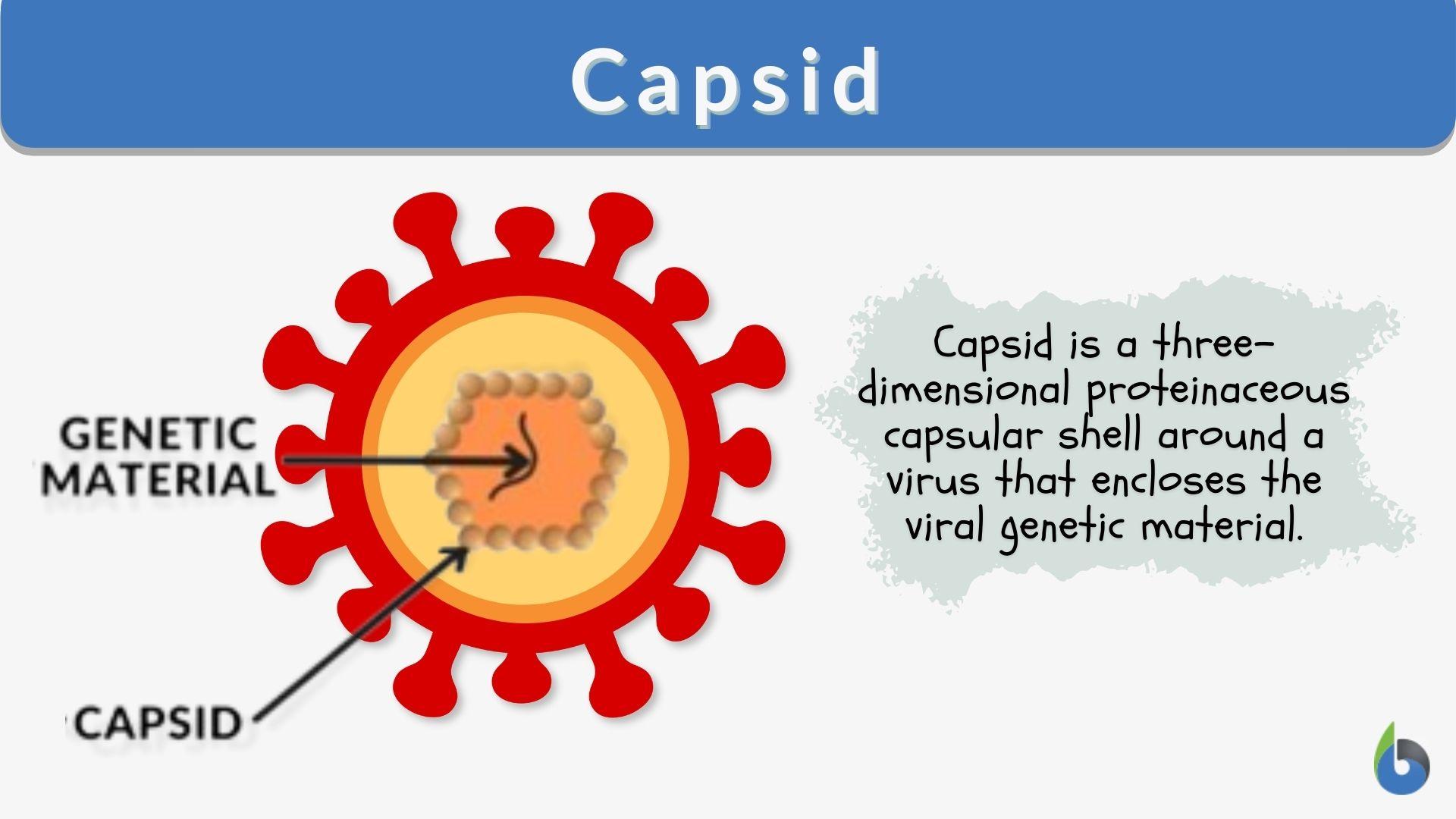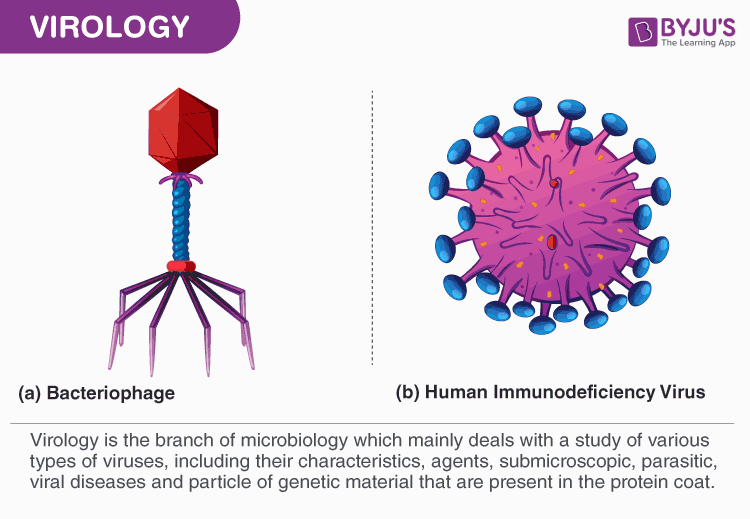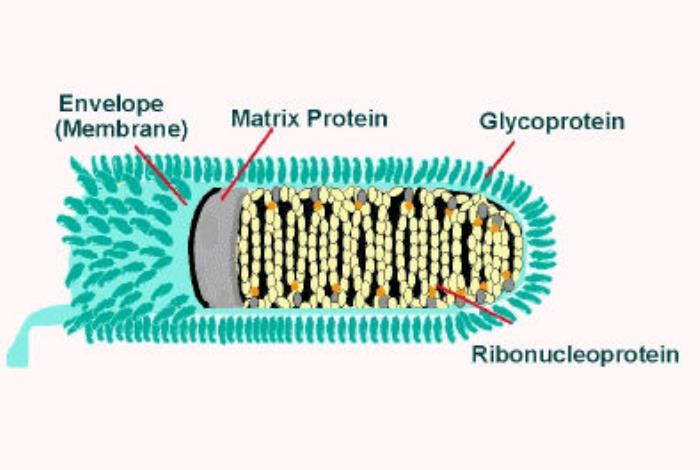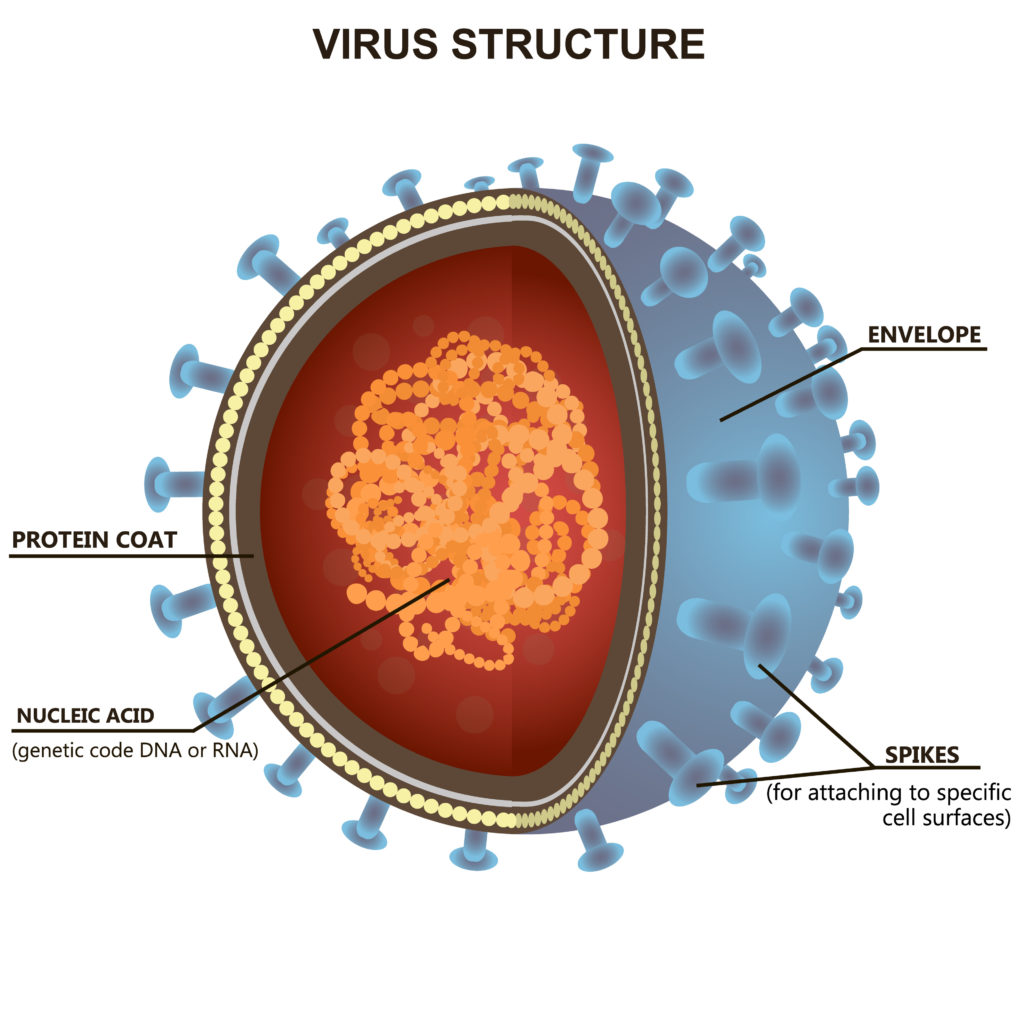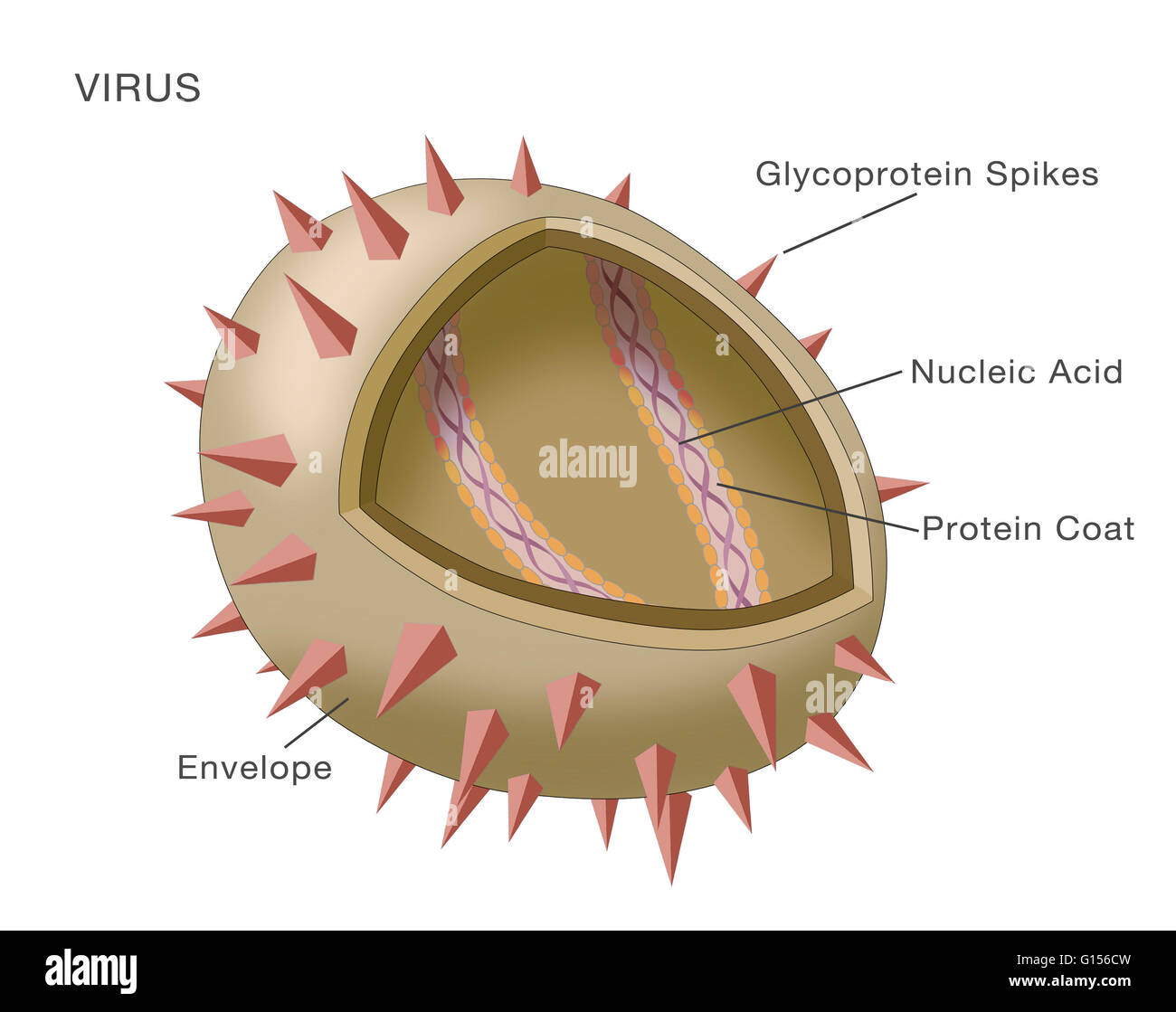
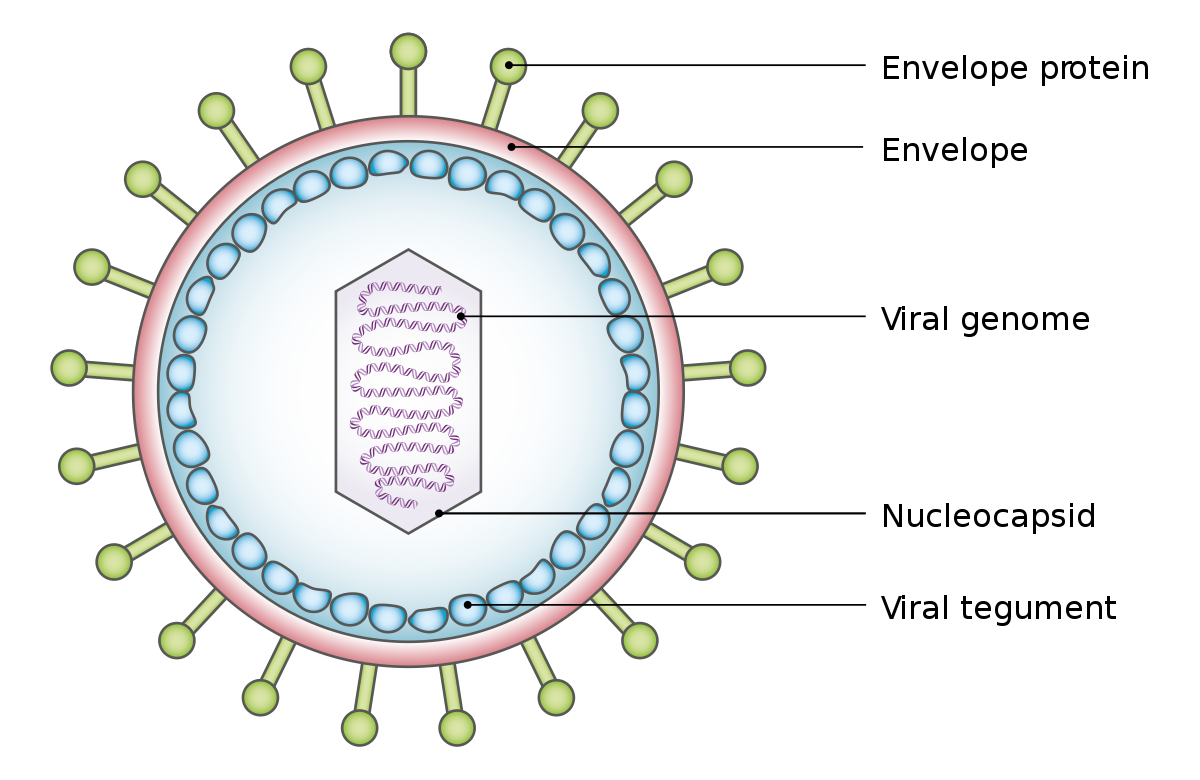
Diagram showing the structure of a typical virus. Virus particles, or virions, generally consist of two or three parts: the genetic material made from either DNA or RNA; a protein coat that

If viruses consist of RNA and a protein coat then can't we produce a drug that will denature the protein coats to destroy the virus? - Quora

Plant Viral Coat Proteins as Biochemical Targets for Antiviral Compounds | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Which of the following statement is incorrectA. Viroids lack a protein coat.B. Viruses are obligate parasitesC. Infective constituent of viruses is the protein coat.D. Prions consists of abnormal folded protein

Viral structure. Viral particle is made up of a nucleus of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat. Conceptual illustrative virus. 3D i Stock Photo - Alamy
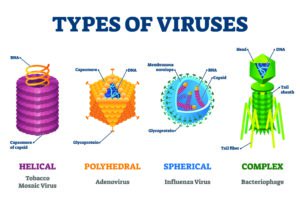
Pandemic Part 1: A Primer on the Biology of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus and the Terminology that You are Hearing - The Pulse